Safety at Construction Site
Bureau Built Constructions
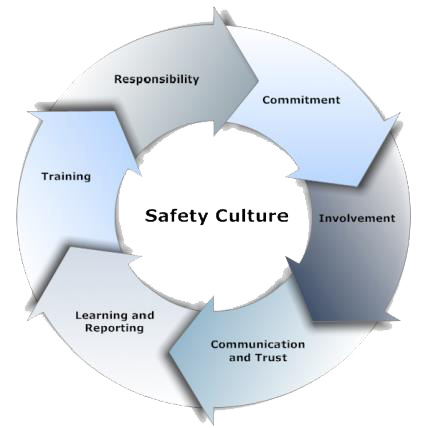
1.0. INTRODUCTION
There are several reasons which influence the safety performance that should be identified and specified in design and pre-construction stage in order to increase safety. With right policies together with safety management associated in design and pre-construction phase one can greatly reduce accidents. One of the ways to enforce this practice is to engage contractors who have proved a record of good safety performance and are conscious of safety regulations. This factor should be considered during the processes of qualifying the contractors and only those with acceptable history of safety performance commitment, should be considered for the project.
While eliminating accidents and work related illnesses is a worthwhile goal, it will never be attained without a proper safety strategy in place. Construction has a number of characteristics making it inherently hazardous. The jobsite is continually changing as construction proceeds and workers do not have fixed worksites and must move around a structure under construction. The tenure of a worker on a site is short, so the worker's familiarity and the employer-employee relationship are less settled than in manufacturing settings. Despite these peculiarities and as a result of exactly these special problems, improving worksite safety is a very important project management concern.
Choice of technology can also be critical in determining the safety of a jobsite. Safeguards built into machinery can notify operators of problems or prevent injuries. For example, simple switches can prevent equipment from being operating when protective shields are not in place. With the availability of on-board electronics (including computer chips) and sensors, the possibilities for sophisticated machine controllers and monitors has greatly expanded for construction equipment and tools. Materials and work process choices also influence the safety of construction. For example, substitution of alternative materials for asbestos can reduce or eliminate the prospects of long term illnesses such as - asbestiosis.
Figure 1 identifies the key factors or elements that consume most safety professionals’ time. These are listed under Job and Organizational Factors. Figure 1 also lists human factors that are not generally considered to be within the scope of a safety professional’s responsibilities. They are typically the job of someone else, such as Human Resources or Organizational Behaviour departments. The importance of human factors in safety excellence is not a new revelation. Many studies have recognized their importance in establishing and maintaining excellent performance. That the safety profession has not more widely recognized and applied these findings to managing health and safety is remarkable.
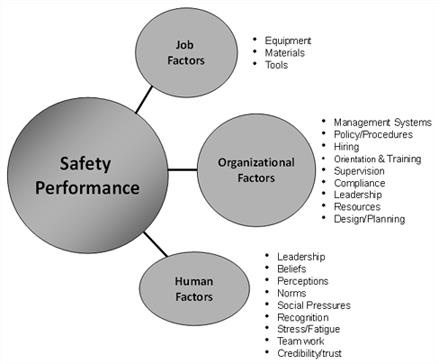
Figure 1
2.0. NINE NEGLECTED SAFETY NORMS
1. Scaffolding
Workers assigned to scaffolding jobs should be properly trained and continually aware of their environment as falling debris, electrocution from power lines, and falls related to unstable platforms can result in serious and other injuries. Supported and suspended scaffolds should be properly outfitted with guardrails to prevent workers from falling from an open side, and workers should be secured in appropriate fall protection. According to the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), scaffolds and scaffold components must be capable of supporting at least four times the maximum intended load.
2. Fall Protection
All employees whose work conditions include the danger of falling should undergo fall protection training regularly. Company training courses should identify specific hazards and familiarize employees with all fall protection equipment used in the workplace. A review of the written prevention and rescue plan will assure employees that help is never far away. Fall protection equipment should be inspected each time it is used and that inspection should be documented. The equipment should be inspected according to manufacturer’s recommendation.
3. Ladder Safety
The misuse of portable ladders can lead to injuries. Ladders should be secured, properly anchored and safely positioned at appropriate angles. Prior to use of these ladders, they should be visually inspected for damaged components including hinges, rungs and side rails. Side rails should extend at least 3 feet above the landing and be secured at the top to a sturdy support. Portable ladders should be used in compliance with the weight standard they are designed to hold and should also comply with stipulated specifications
4. Personal protective equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is worn to reduce workers exposure to occupational hazards and is required to be available on-site. In fact, new regulations now dictate that where PPE is required, employers are now responsible for providing it. Otherwise, employers are ultimately responsible for determining the level of PPE their employees use for optimum protection. Hard hats, eye, ear and hand protection, earplugs and other protective equipment provide protection from falling objects, head injuries, sparks, dust/fragments and burns. Unfortunately, many workers choose to forgo this level of protection due to discomfort or disinterest. In response to this issue, many safety distributors now offer a range of comfortable and more fashionable gear to choose from, including eyewear that resists fog and prescription-strength safety glasses.
5. First aid and fire safety
It is common sense that first aid and fire safety are key programs on any given job site. However, many sites lack enough first aid stations, kits and materials such as gauze, bandages, ice packs, burn ointment and eyewash stations. Similarly, fire extinguishers should be kept in ample supply, regularly inspected and used for the type of fire they are effective on. Workers should be adequately trained about fire hazards on the construction site and what to do in an emergency. Fire emergency plans should outline the assignments of key personnel, provide evacuation routes and be reviewed regularly.
6. Confined spaces
Working in confined spaces can be an inconspicuous risk, as fatalities most often occur due to invisible circumstances such as oxygen-deficient, toxic or combustible atmospheres. Also known as permit-required confined spaces, they should be tested prior to entry and continuously monitored using a properly configured and calibrated monitor. The monitors, once connected to a docking station, also help maintain a proper calibration record for these confined spaces.
7. Record keeping
Maintaining up-to-date records of equipment inspections and injury logs is not only important, but is also the best way to protect employers from legal ramifications in the event of injury and death.
8. Welding safety
Welding injuries, from minor flash burns to eye injuries, can be painful and cause disfigurement or career-ending disabilities. Wearing the proper PPE is an easy way welders can protect themselves against these risks and preserve their livelihood. Unfortunately, overconfidence leads welders to think they are immune to such
injury, or they may choose not to use PPE because it is too expensive or the job is too small. Some welders under-protect themselves because they feel the PPE is too warm or restrictive to wear. Fortunately, workers now can find new PPE garments made of lightweight materials that wick away sweat to stay comfortable. Welders now have many options in materials, flame-retardant traits, fabric weight and accessories to suit up for the job. Welding helmets should be equipped with the proper filter lens in either a passive or an auto darkening style to shield against the arc’s bright light.
9. Training
The key to preventing many workplace accidents and injuries is frequent and effective employee training programs. These programs exist for virtually all construction safety components including fall protection, fire safety and welding safety among others.
3.0. DIFFERENT CAUSES OF CONSTRUCTION ACCIDENTS
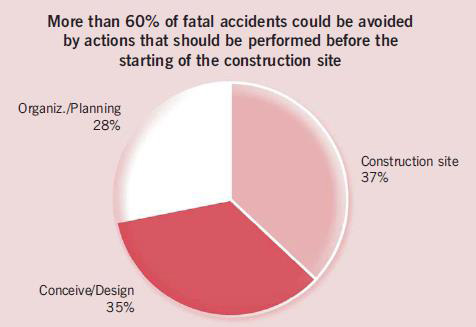
There are various things which could potentially cause a construction accident. Sometimes, machinery and tools can malfunction, leading to injuries. Based on the various tasks being performed at the site, there can also be the chance of exposure to toxic chemicals, dangerous debris, falling objects, or hazardous materials. There may also be accidents that occur due to negligence, like when tools are not properly put away or supports aren’t safely secured. Sometimes, accidents can happen as a result of mis judgments, including each time a too-short ladder is used. Construction sites often times have many areas that are inherently unsafe, including holes floors, partially constructed building components, or areas including dangerous exposed surfaces.
Chemical accidents, gas explosions, and electrical accidents all can happen on construction sites. While it’s not hard to observe how these situations can be dangerous for those who are on the job at a construction site, sometimes accidents will even involve folks who are simply walking close to the site. Chemicals, dust, malfunctioning tools, and falling objects can all be the cause of unsafe conditions at or near a construction site. Someone who is just walking down the sidewalk could find themselves injured because of an accident. A Sacramento personal injury lawyer has the experience and knowledge you’ll need so that you can deal with the complicated legalities that often originate from a construction accident.
4.0. CONSTRUCTION HAZARD
Hazard is defined as potential situation that may cause unintentional injuries or deaths to people, or damage to, or loss of an item or belongings. Therefore the estimation of the safety level at construction sites can be applied by specifying all on-site hazardous elements. Therefore, Safety performance of each element should then be studied and measured by evaluating the relevant on-site hazard factors. “By reducing the potential hazard of elements, its safety performance improves considerably” says Aref Charehzehi, Department of Structure and Materials, Faculty of Civil Engineering, University Teknologi Malaysia (UTM), Johor Bahru, Johor, Malaysia.
On the other hand, safety development in the construction industry occurs only when all workers in the operation of construction sites change their behaviour, respect to regulations and try to improve safety level in their personal activities. Moreover, the management support to the workers is also very important in providing the best solution for the safety related problems.
5.0. DEVELOPMENT OF SAFETY PERFORMANCE
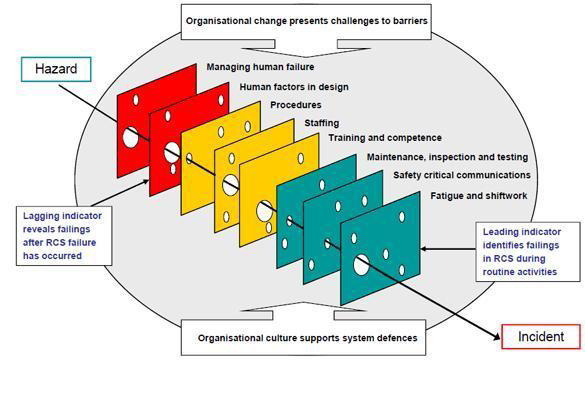
A common approach for prevention of construction accident is to predict the upcoming event under given circumstances. The accuracy of such predictions is based on knowledge about past accidents. It has been proved that the main reasons for accidents in the construction industry are resulted from the unique nature of the industry, human behaviour, difficult work-site conditions, and poor safety management which result in unsafe work methods and procedures.
There are three main reasons for preventing the construction accident;
- Humanitarian Reason- to ensure that people are safe and healthy at work and nobody suffers from accident due to the work activity.
- Legal Reason- to comply with provisions of law which, specify standards to ensure safety and health at work.
- Economic Reason- to prevent losses due to accident in term of expenses on medical, compensation, property damage, downtime, etc.
6.0. RISK ASSESSMENT AND CONTINUOUS SAFETY
Following are the six steps on Risk Assessment and Continuous Safety Improvement:
Step 1: Creating safety and health regulation
Safety policy is contained some notification that exhibit responsibilities, commitments, culture, behaviour and requirement to ensure that a workplace is safe, healthy and acceptable. So this statement will encourage all the employees and other people in the site that are affected by the site condition to pay attention to these notifications to increase safety performance. The responsibility of this policy is as below:
- Create a condition to ensure that workers are operating in safe and healthy environment.
- Decline the situation that cause to create risk.
- Provide safe tools and equipment.
- Provide reliable method and procedure for doing work.
- Provide needed information, training, and instruction regarding to site condition and type of the construction project.
- Emphasize to use suitable clothe and safety equipment.
- Assign personnel according to their ability and skills.
- Create compulsory entrance regulation to site for regular people.
Step 2: Identify the Hazard
Hazard can cause different injuries to the workers and sometimes can cause death. Therefore, identifying the hazard is important to control risk and decreasing accident in site. In site all the materials, equipment, machineries, and also work activity can cause hazard. Therefore, we have to evaluate work place and work activities to identify hazards or find the resource of hazards. Hazards can be physical, healthy, chemical, biological, and humanitarian.
Some regular causes of physical hazard are falling from scaffold, moving heavy burden manually, cutting by machine, burning by firing materials, straining, injury by another person and etc. while chemical hazards are related to chemical materials that are utilized in a project such as glues and correction fluids to industrial solvents, dyes, and acids. Regulation is required for using chemical materials by workers. This regulation should create according to effect of chemical materials on skin that is initial problem and also examine long term effect of these materials.
Biological hazards contain every kind of viruses and bacteria that may lead infection and substances from animals that can cause health problems. Therefore, biological regulation for more protection and increase safety is required.
Human factors are related to the mental and physical capacity of the worker. Workers must have the ability to do their duty and work place and system should be comfortable and without stress. For instance, pregnant women, people with disabilities, older worker, or young worker with no experience have higher accident rate.
All the employees must be informed about the hazards that can existence in the site regarding type of work. Record of previews accident, experience of the expert people, and different kind of standards can assist employees to determine the resource of hazard. Furthermore, we can use professional people to provide safety
statement and identify hazards but the advisor is required to know about the situation, kind of work and must have an adequate experience.
Step 3: Assessment and evaluation of risk
Possibility of harm to the people by hazard is risk that has different severity and frequency. Risk is also related to the number of people who will be affected by hazard. The magnitude and serious of the harm and also the number of the worker that are affected is important for assessing risk. Risk assessment must be done by own employees in the work therefore, if the experience and expertise of the worker is not enough, the company must provide the competent person to assist them. There is different quantitative and qualitative risk assessment that we have to choose suitable one regarding to the project and site condition.
Step 4: Decide What Precautions Are Required
You have to use proper method and tools regarding the situation to preventing risk. Law requirement is one of the important strategies that must be followed by all the employers. Law is going to make a guideline on how evaluate the risk and increase safety. Most of the times improving safety and start to protect from the hazard is no so expensive but it is creativity, for example using non slip material in slipper surface or sometimes change the method and procedure to do the work can be useful and effective. Some of the precaution is as below:
- Reliable and clean work condition.
- Using safeguard in high level.
- Using skilled worker.
- Enough training for worker.
- Provide reliable inspection.
- Availability of emergency aid.
- Availability of protective equipment.
Step 5: Record Finding
All the finding of the risk assessment must be record in safety statement. It means mention more hazard and dangerous situation that can affect employees in workplace. Therefore, company rule, manufacturing instruction, and choosing appropriate attitude is related to these records. This finding must be update and related to the work position because of increasing safety and also decline risk.
Some documents that can assist us to add several useful notifications to the safety policy which is utilized in the organization are according to the following:
- Manual instruction of materials and plants.
- Company regulations.
- Operating instructions.
- Manufacturers’ instructions.
- Company safety and health procedures.
Step 6: Review and Update
Using safety statement should be one of the important parts of the work and everyday this statement should be available for inspection in the workplace. This statement should be obvious and relevant to the work. Significant change in workplace or kind of the work that can add new hazard to the employee cause to provide new statement related to these hazards. Employees are responsible to amend safety statement if necessary.
Sometimes employee cannot do it and should take help from professional persons. Employee should consider some important issues to revise safety statement as below:
- Safety statement must be related to the work condition.
- Examine hazards, risks, risk assessment and identify essential safety protector.
- Use practical methods to implement in site.
- All the notification should be according safety and health performance standard.
- Consider all the humanitarian, legal, and economical reason for preventing hazard and risk.
- Examine how can improve safety and health performance.
Reference
Enhancement Of Safety Performance At Construction Site-Aref Charehzehi 1, Alireza Ahankoob2; Department Of Structure And Materials, Faculty Of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (Utm), Johor Bahru, Johor, Malaysia.